- Full Research Paper
- Open Access
- CCA40 Inter’l Lisence
- Not for the profit
Scientific and Technical Advisory Council (STAC), of the Special Journals Publisher (SJP)
*******************************************************************
Citation:
Scientific and Technical Advisory Council (STAC) of the Special Journals Publisher (SJP): Conceptual framework in Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics Research. Special Journal of Engineering, Physics, Mathematics and Statistics, [SJ-EPM], 2020; 1 (1):1-19
Correspondence: editorialoffice@spparenet.org
************************************************************
Background
A concept is an idea notion, thoughts, perception or impression about something or anything. It may be about a question, problem, challenge, strength, success or more. A framework is an outline, agenda or background of anything (1). So, the concept of Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research or framework of a research may be seen as the idea notion, thoughts, perception or impression of a research or investigation whereas the framework of the research is the outline, agenda or background of the research. (2)
Therefore, the conceptual framework of Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research is the outline or agenda of the researcher’s idea, notions, perception and the research or investigation (3). In other words, conceptual framework may be seen as the entire, reasonable direction and associations of research ideas that forms the fundamental intellectual, structures, plans and practices and implementation of your whole research project. The conceptual framework defines the complete package made of the Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics researcher’s thoughts channeled towards the identification and mastery of the research: topic, problem, questions, literature, theories, methodology, the methods, procedures and instruments, the data analysis and interpretation of findings, recommendations and conclusions (4).
According to Miles and Huberman (5) a conceptual framework or concept map pulls together, and make visible, what your implicit theory is, or to clarify an existing theory. This can allow the Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics researcher to see the implications of the theory, its limitations, and its relevance for study. Again, it helps to develop theory and Like memos, concept maps are a way of “thinking on paper”; they can help Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics researchers see unexpected connections, or to identify holes or contradictions in your theory and figure out ways to resolve these. Concept maps usually require considerable reworking to get them to the point where they are most helpful (6)
Concept map development
To develop a concept map in Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research, a set of concepts to work with is needed knowing that it is all about trying to represent already existent theory you already have about the phenomena you are studying, not primarily to invent a new theory (7). On the other hand, topic key words probably represent important concepts in theory of Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research being implemented (8). Some of these Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research concepts can be pulled directly from things already written about a research topic under investigation. These may serve as a way of broadening the scope and spectrum of coverage of research area
Existent topic in Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research may be used as a example in which already written topic may be used a s template to map out the theory that is implicit (or explicit) in this topic. One key concept, idea, or term may be taken and an effort made to brainstorm on all of the topics themes and subthemes that might be related to this (9). Thereafter, efforts are made to scale down, the Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research topics and only those that seem most directly relevant to a study under investigation may be studied.
The selected topic is placed under scrutiny by asking someone to review the topic under investigation to help point out areas of bias about Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics researchers topic. Concepts are not to be ignored based on personal experience rather than the literature as these can be central to a conceptual framework. Strauss (10) and Miles and Huberman (5) provided additional advice on how to develop concept maps for your study. Once an Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research concepts is generated, then efforts are made look for how the concepts are related or what connections exist among them.
Rational
It is true that many publishers and authors have the right to present their research report in one way or the other, one thing stands out that in all Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research a generally good paper include the one that has a very clear concept map making it clear for readers to locate the point of argument and what authors have achieve or tried to achieve in the paper. The significance of conceptual map or framework in Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research cannot be over emphasized and this applies to all disciples or events for which reliable answers are needed for critical questions.
Objective
In this Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research study efforts were made to review in retrospect activities and updates taking place in the research world over the past 3 decades with the ultimate goal of showing the significance of conceptual framework in research
Materials and Methods
In this retrospective cross-sectional study, we downloaded and perused 486 published full-length original papers, published addendum, corrections, editorials, abstracts of meetings, conference proceedings, and review article, on the general concept of development and sustainability. This searching and corresponding download of relevant papers were made from globally recognized research-based data repository that included but not limited to the Web of Science (WoS) (11) core collection database on the nineteens of July 2020 at about 10.25 GMT+2). The database of PubMed, Research gate and Google scholars were perused to be sure no new documents relevant and necessary for this study were missed out. However, the web of science formed the major and reference database for this study because our software was more compatible to recovered data encoded in the web of science database while other databases consulted served to provide other relevant articles, we considered imported but probably missing in the web of science.
Boolean topic search approach
The Boolean topic search approach (12) used included “(development * AND sustainability$) OR (Sustainability of * AND development$) to encompass all relevant and available documents (13) on the subject of development and sustainability between 1990 and 2019. At the time of this study, we judged that the Web of Science Core Collection database had enough use friendly and accessible academic research database relatively covering enough journals, books, conferences as well as millions records from clarivate.libguides.com (references). To ensure the inclusion of abbreviated or shorten words, the wildcard * and $ were added to the end of the search algorithms. Thereafter, all document that meet the eligible criteria of sustainable development were retrieved and exported into BibTex file format and the authors, titles, abstracts mined in PDF file format.
Data analysis
All the bibliometric variables were retrieved filtered and normalized for quality control. The results were analyses in bibliophagy plug in package of 3.5.1 version of R-studio software, while the codes and commands were adopted from Https://www.bibliometrics.org to evaluate the bibliometrics indices. Tables and graph were made in Microsoft excel 16 version and network maps were visualized in 1,6 Vox-viewer software
Results
In this study, 409 papers written by 1425 authors over a period of three decades were recovered, perused and analyzed as shown in table 1. Ninety-nine (99) documents were written by 96 authors while 1329 authors wrote 1230, multi-author documents giving 3.62 collaborative index. Authors and co-authors per documents indexes were 3.48 and 3.62 respectively. Two hundred and eighteen (218) documents were full length articles. Twenty-nine book chapters and 10 proceedings papers were originally presented as articles. Fifty-two (52) proceedings papers, 56 reviews, three of them were originally presented as journal articles while 18 were editorial materials and 18 articles were Editorial documents respectively.

From the figure1, conceptual framework received the biggest category allotment followed by research agenda, health, nursing, case study, and determination. Literature review was the next biggest category allotment and the associated variables included research, decision making, framework, bibliometrics and competitive advantage. The next category is innovation and associated variables included, sustainability, prevention, creativity, clinical research and electronic health records. The next category was qualitative research and the corresponding variables included evaluation, Africa, knowledge management, women, data privacy and communication. Collaboration and quality of life had equal category size allotment with variables of collaboration including: primary care, systematic review, critical appraisal, knowledge, action research, and epistemology whereas experiential learning, Asia, comorbidity, leadership and data repositories as the associated variables. Risk is the next category and associated variables included cooperate social responsibility, outcomes, higher education, China and ecosystems respectively
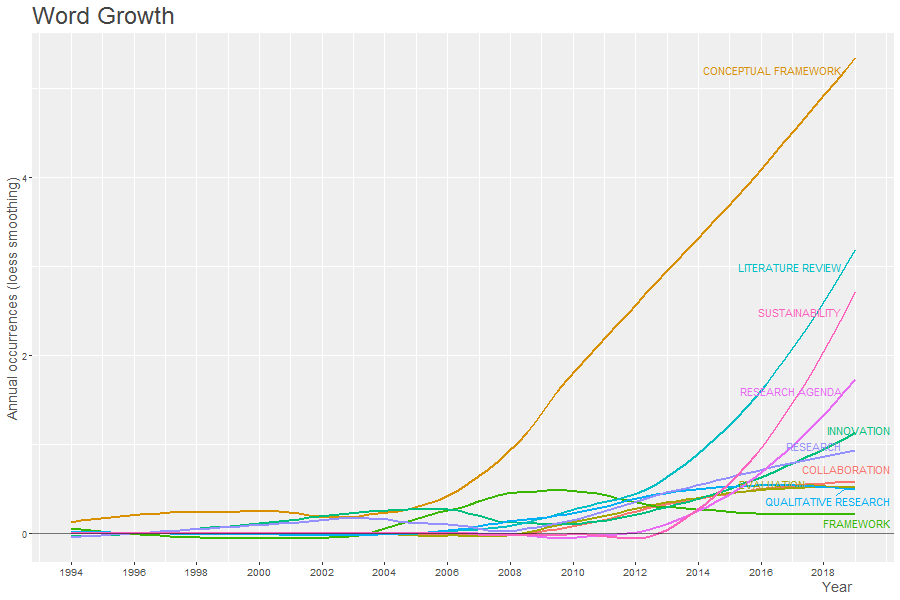
Figure 2: The word growth graph shows word usage in the studied period as relates to conceptual framework and research. While frequency of words used remained relatively stable from 1994 to 2004, the use of conceptual framework experienced a hype as seen in a steep rise from 2008 till 2018. All other words used remained relatively stable and low in occurrence from 2004 till 2014, thereafter literature review, sustainability, research agenda and innovation as shown in the fig above.

Figure 3: The trend of topics used in research involving conceptual framework are shown in the above figure. The use of words in research experienced the greatest 4-fold logarithmic growth between 2014 and 2018 with governance, participation, and context being at the base of the topic trend while management, model and impact were on top of the topic trend. Terminologies that saw a two-fold rise included information, systems, outcomes, policy, innovations, community, firms among others. Between 2008 and 2010, biodiversity, consequences’, experiences, United states, experienced less than 2-fold log rise in occurrence.

Conceptual framework cooccurred with literature review, research agenda, prevention, research, nursing, women, and heath. Among the conceptual framework variables, literature review had the strongest relationship with research while nursing, prevention, women, heath, and research agenda had similar relationship with literature review.

In the figure 5 above, there are 3 main clusters, the blue, green and red clusters. The green cluster located in the North-East quadrant of the multiple comparison analysis of the conceptual structure map MCA/CSM which represents positive conceptual framework that is strongly related to the associated variables such as: performance, competitive advantage, governance, perspective, context, management, and information technology, all clustered in a distance considered most discriminatory to the conceptual framework and research.
To further interpret the observed category and variable relationship nested within the north east quadrant, the distance from the central category to the variables depicts strength of relationships with the closest having a stronger relationship than the distant variables. Therefore, in the green words cluster: conceptual frame work map is strongly related to knowledge and weakly related to resource-based view, networks, organizations, and technology
The green cluster in the south eastern quadrant depicts presence of inclusion and diversity weekly related to perspective, identity, business, construction, and firm performance.
Finally, the red cluster lies between the south west and the north west quadrant depicting no inclusion and diversity and the associated variables are relatively normally (neither strong or weak) associated the listed variables. However, within the red cluster, nested within the south west and north west quadrant: faculty, women, medicine, care, cultural competence, improving diversity, African Americans, climate, workplace and leadership are all distantly discriminated against inclusion and diversity compared to closely related experience education, science, gay, discrimination, schools, minority in figure 7

From the figure 6 of topic dendrogram above, community and design are related to each other while strategies and firms are related to each other. However, community/design is different from strategies/ firms. Information technology and knowledge are similar but not similar to completive advantage. Context and performance are similar bit different from management and technology. On the other hand, risk and sciences are similar, but different from policy. Consequences and quality are similar but different from behavior. Organizational culture and program are similar but different from trust and systems Experience is similar to life but different from challenges. And so on

The bubbles represent authors, the size of the bubbles represent the magnitude or number of publications. Line between authors represent coauthorship links, line between two authors or bubbles shows that those authors have coauthored one or more articles, authors that have coauthored articles tend to be located close to each other. Colors indicates clusters of authors that are connected by coauthorship. The figure above shows there were relatively no collaboration but the bubbles overlap may indicate coauthorship connection between authors. Authors on the left of the figure relatively low number of articles with no collaboration and no coauthorship.

The figure above shows there were relatively no Institutional collaboration that is outside a given location since there is no line linkage. However, bubbles overlap shows size overlap and may not indicate any consortia of collaboration.

The figure above shows there were collaboration between countries. United Kingdom collaborated more with other counties followed by USA. Other counties were all connected to either USA or UK but rarely to each other. Three main clusters can be seen the blue, purple and red. United Kingdom, worked more with Netherlands, and France, then followed by Kenya and Italy, and by Belgium, Sweden, and Finland. USA worked more with Switzerland, Ireland and South Africa followed by Bangladesh, Pakistan, Columbia Mexico, India and China. The red cluster is between Germany Japan and Spain. And the green cluster is between New Zealand Australia and Canada
Discussion
Emergence of complex health epidemics and pandemics (14) continue to emphasize the need for research alertness if humans are to continue living on the planet earth (15). Treatment failure poses a great challenge to successful diseases interventions especially during epidemics. There are ample literature widely confirming that resistance to treatment agent, compliance to treatment directives and prescription, holds the key to effective intervention (16). Treatment failures and management complications (17) continue to stress the need for Mathematical and statistical disease modelling (18) and thereby underscoring the need for Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research (19). The need for a good conceptual framework that will help a carefully designed researched to achieve its set objective cannot be over emphasized. Therefore, a description a good concept is necessary.
Multidisciplinary Research directions
Conceptual framework of research in diseases epidemiology involves multidisciplinary questions that appears to hold the key for success in the design and implementation of effective intervention. Practical issues to be addressed from all aspects of research using some relevant questions involving Engineering, Mathematics or Statistics may lead to better outcome. With research advances we now know better about the relationship between the structure and properties of materials, for the benefit of mankind and his economy; (20)
Teflon is a product of modern research advancement, found in everything from cookware to apparel to medical transplant materials (21) that has increased human adaptation to his environment on the planet earth The design and safe use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), has led to more efficiency in research outcome of many interventions (22), Design and use of tomographic studies such as computed axial tomography (CAT scan); Positron Emission Tomography (PET), and x-rays, mammography equipment, and radiation (23) has demystified the myth behind complex diseases making intervention and management a mere routine practice
data can now be predicted from systematically formulated algorithms, (24), mathematical modeling and statistical algorithms can now be used to arrive at optimal or near-optimal solutions to complex problems in many research disciplines. (25), Statistics can now be used to explain the science of statistically explaining and altering of mental processes and behaviors in humans. (26)
Interactive decision aids have been developed to assist in the analysis of decision problems with multiple and conflicting objectives so as to maintain the supremacy of man over the existential challenges that faces him daily (27), Statistics can now also help in conservation decision making, climate change, understanding of biodiversity patterns, evolutionary ecology and macroecology, an advancement that man desperately need to maintain an edge with respect to sustainable development (28)
Elements of concept map
for Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics Conceptual map (29) has 4 unique elements, namely: concept, lines/arrows, linking words, and proposals. A concept is that word that is used to identify facts, processes, objects or situations that share the same characteristics, and differentiate them from those that are different from them (30). Lines and arrows are used, within a conceptual map, to represent the connection between one concept and another (31). Linking words are short descriptions that are located between one concept and another, next to the lines that connect them, with which the way in which concepts are related. Concept maps are time schemes containing preselection, presentation of information in segments which are later integrated. for Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics Concept maps answers questions which helps build knowledge (32). When new knowledge is gained, stakeholders appreciate elaborate approaches to things and strive to implement it, leading to negotiation of meaning and self esteem
There are so many ideas that comes in and goes out in researchers mind but it should be noted that not all these ideas are researchable. The decision on which thoughts or idea should be studied are based on many premises but the most outstanding are challenges to: advancement, wellbeing, existence, supremacy and more. Advancement is a broad term that may include but not limited to knowledge, technology, economy, and many other interests. Wellbeing covers health, social, economic and environmental. Existence challenge deals with survival from extinction while supremacy challenge deals with fame, power, respect and more. Care and caution are needed when sieving through information to know what to study or investigate to confirm a concept.
Information quality for concept map development
Quality of for Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research information considered when designing a good concept include, relevance, faithful representation, Neutral, comparable, verifiable, concise, timely, Relevant ideas keeps the research in focus to the objective and prevent frivolities and waste of resources and increase the feasibility of the study. Correct representation gives the true picture of the idea in real terms with no fabrication, falsification or extrapolation. Neutral idea is not swayed to the left or right and mostly remain in the center but subsequently impacts both left, right and center. Nature and quality of ideas are defined by its comparable, verifiable, concise and timely characteristics. These are the basis for which a good concept map or framework is made.
Such terminologies include but not limited to: Creativity, innovations, research design, experiential learning, framework, knowledge management, competitive advantage, organizational culture, collaboration, qualitative research, action research, collaboration, quality of life, Africa and Asia, China and others. These are terms that can come to mind when conceptualizing a research study in Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics. In Figure 2, management, model and impact were on top of the most trending topics. Many of the Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research are tested on experimental models, and the outcome of the experiments definitely has impacts on disease management in the long or short term.
In deceasing order of magnitude, conceptual framework cooccurred with literature review, research agenda, prevention, research, and more fig 4. In Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research, the first step is to conceptualize the research, look for literature to determine its relevance in the research world stage, develop an agenda of the research and implement the research in such as a way as to achieve the ultimate goal of disease prevention. Among the conceptual framework variables, literature review had the strongest relationship with research depicting the strength and influence of literature review in Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research both of which remain strong variables to conceptual frame work.
There was little or no authors and institutional collaboration figures 7 and 8. Probably depicting the challenges and road blocks militating against Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research. However, collaboration was noticed at country level with United Kingdom and United states playing major role in synchronizing global research agenda especially in the context of Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research.
As a master plan, which a conceptual framework is, some questions are necessary in the context of Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research, and needs answers for a good concept to be produced. The questions include but not limited to the following: what the researcher wants to do in the context of Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research? (33) Why he or she wants to do it with respect to importance, target, objective, and spectrum of coverage in Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research? How the researcher wants to achieve its objective with respect to methods, participants, sampling and data analysis, interpretation of data, worldview of data with respect to positive or interpretative, critical or pragmatic paradigm in the context of Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research? How will the report or publication of the findings be with respect to: a research paper, seminar paper, a conference paper, a book chapter, a book or thesis in the context of Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research?
Conclusion of the research concept map
The Conceptual framework is important in research, provision of the fundamental principle for setting up a standard for Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research, enhancement of consistency and comparability, generally accepted criteria and principles governing science disciplines are ascertained. such as Engineering, Mathematics and Statistics research. The objective identifies the goals and purpose while the fundamental provides the how to achieve the objectives.
References
- Palazuelos D, Ellis K, Im DD, Peckarsky M, Schwarz D, Farmer DB, Dhillon R, Johnson A, Orihuela C, Hackett J, Bazile J, Berman L, Ballard M, Panjabi R, Ternier R, Slavin S, Lee S, Selinsky S, Mitnick CD. 5-SPICE: the application of an original framework for community health worker program design, quality improvement and research agenda setting. Glob Health Action. 2013 Apr 3;6:19658. doi: 10.3402/gha.v6i0.19658
- Chun Tie Y, Birks M, Francis K. Grounded theory research: A design framework for novice researchers. SAGE Open Med. 2019 Jan 2;7:2050312118822927.
- Sovacool BK, Hess DJ. Ordering theories: Typologies and conceptual frameworks for sociotechnical change. Soc Stud Sci. 2017 Oct;47(5):703-750.
- Amanda C. Jozkowski(2017) Reason & Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research, 2nd Edition (2017), Occupational Therapy In Health Care, 31:4, 378-379,
- Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded source book (2nd ed.). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
- Carr-Lopez SM, Galal SM, Vyas D, Patel RA, Gnesa EH. The Utility of Concept Maps to Facilitate Higher-Level Learning in a Large Classroom Setting. Am J Pharm Educ. 2014 Nov 15;78(9):170.
- L Allen M, Schaleben-Boateng D, Davey CS, Hang M, Pergament S. Concept Mapping as an Approach to Facilitate Participatory Intervention Building. Prog Community Health Partnersh. 2015 Winter;9(4):599-608. doi: 10.1353/cpr.2015.0076.
- Lynch EA, Mudge A, Knowles S, Kitson AL, Hunter SC, Harvey G. “There is nothing so practical as a good theory”: a pragmatic guide for selecting theoretical approaches for implementation projects. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018 Nov 14;18(1):857.
- Maxwell L, Odukoya OK, Stone JA, Chui MA. Using a conflict conceptual framework to describe challenges to coordinated patient care from the physicians’ and pharmacists’ perspective. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2014 Nov-Dec;10(6):824-836.
- Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. (1990). Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory procedures and techniques. Newbury Park, CA: Sage
- Sevinc A. Web of science: a unique method of cited reference searching. J Natl Med Assoc. 2004 Jul;96(7):980-3.
- Bramer WM, de Jonge GB, Rethlefsen ML, Mast F, Kleijnen J. A systematic approach to searching: an efficient and complete method to develop literature searches. J Med Libr Assoc. 2018 Oct;106(4):531-541. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2018.283. Epub 2018 Oct 1.
- Chatterjee A, Ghosh A, Chakrabarti BK. Universality of Citation Distributions for Academic Institutions and Journals. PLoS One. 2016 Jan 11;11(1):e0146762.
- Madhav N, Oppenheim B, Gallivan M, et al. Pandemics: Risks, Impacts, and Mitigation. In: Jamison DT, Gelband H, Horton S, et al., editors. Disease Control Priorities: Improving Health and Reducing Poverty. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 27. Chapter 17.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525302/
- Mogilever NB, Zuccarelli L, Burles F, Iaria G, Strapazzon G, Bessone L, Coffey EBJ. Expedition Cognition: A Review and Prospective of Subterranean Neuroscience With Spaceflight Applications. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018 Oct 30;12:407.
- Simoni JM, Amico KR, Pearson CR, Malow R. Strategies for promoting adherence to antiretroviral therapy: a review of the literature. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2008 Nov;10(6):515-21. doi: 10.1007/s11908-008-0083-y.
- Kazmi RS, Lwaleed BA. New anticoagulants: how to deal with treatment failure and bleeding complications. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;72(4):593-603.
- Ventola CL. Current Issues Regarding Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) in the United States: Part 2: Regulatory and Safety Concerns and Proposed Governmental Policy Changes with Respect to Dietary Supplements. P T. 2010 Sep;35(9):514-22.
- Colon-Berlingeri M, Burrowes PA. Teaching biology through statistics: application of statistical methods in genetics and zoology courses. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2011 Fall;10(3):259-67.
- Kohn KP, Underwood SM, Cooper MM. Connecting Structure-Property and Structure-Function Relationships across the Disciplines of Chemistry and Biology: Exploring Student Perceptions. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2018 Jun;17(2):ar33.
- Shuster KA, Brock KL, Dysko RC, DiRita VJ, Bergin IL. Polytetrafluoroethylene toxicosis in recently hatched chickens (Gallus domesticus). Comp Med. 2012 Feb;62(1):49-52. PMID: 22330651; PMCID: PMC3276392.
- van Beek EJR, Kuhl C, Anzai Y, Desmond P, Ehman RL, Gong Q, Gold G, Gulani V, Hall-Craggs M, Leiner T, Lim CCT, Pipe JG, Reeder S, Reinhold C, Smits M, Sodickson DK, Tempany C, Vargas HA, Wang M. Value of MRI in medicine: More than just another test? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Jun;49(7):e14-e25.
- Cahan EM, Hernandez-Boussard T, Thadaney-Israni S, Rubin DL. Putting the data before the algorithm in big data addressing personalized healthcare. NPJ Digit Med. 2019 Aug 19;2:78.
- Officers of the SIAM Activity Group on Computational Science and Engineering (SIAG/CSE), 2013-2014. Research and Education in Computational Science and Engineering. SIAM Rev Soc Ind Appl Math. 2018;60(3):707-754
- Bohr A, Memarzadeh K. The rise of artificial intelligence in healthcare applications. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. 2020:25–60.
- National Research Council; Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education; Commission on Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education; Committee on Basic Research in the Behavioral and Social Sciences; Gerstein DR, Luce RD, Smelser NJ, et al., editors. The Behavioral and Social Sciences: Achievements and Opportunities. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1988. 5, Methods of Data Collection, Representation, and Analysis.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546485/
- Committee on Improving the Quality of Cancer Care: Addressing the Challenges of an Aging Population; Board on Health Care Services; Institute of Medicine; Levit L, Balogh E, Nass S, et al., editors. Delivering High-Quality Cancer Care: Charting a New Course for a System in Crisis. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2013 Dec 27. 3, Patient-Centered Communication and Shared Decision Making.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK202146/
- Bellard C, Bertelsmeier C, Leadley P, Thuiller W, Courchamp F. Impacts of climate change on the future of biodiversity. Ecol Lett. 2012 Apr;15(4):365-377.
- Novak, J. D. & A. J. Cañas, The Theory Underlying Concept Maps and How to Construct and Use Them, Technical Report IHMC CmapTools 2006-01 Rev 01-2008, Florida Institute for Human and Machine Cognition, 2008, available at: http://cmap.ihmc.us/docs/pdf/TheoryUnderlyingConceptMaps.pdf
- Schoonenboom J, Johnson RB. How to Construct a Mixed Methods Research Design. Kolner Z Soz Sozpsychol. 2017;69(Suppl 2):107-131.
- Mammen JR. Computer-Assisted Concept Mapping: Visual Aids for Knowledge Construct. J Nurs Educ. 2016 Jul 1;55(7):403-6.
- Hung CH, Lin CY. Using concept mapping to evaluate knowledge structure in problem-based learning. BMC Med Educ. 2015 Nov 27;15:212.
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Policy and Global Affairs; Committee on Science, Engineering, Medicine, and Public Policy; Board on Research Data and Information; Division on Engineering and Physical Sciences; Committee on Applied and Theoretical Statistics; Board on Mathematical Sciences and Analytics; Division on Earth and Life Studies; Nuclear and Radiation Studies Board; Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education; Committee on National Statistics; Board on Behavioral, Cognitive, and Sensory Sciences; Committee on Reproducibility and Replicability in Science. Reproducibility and Replicability in Science. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2019 May 7. 5, Replicability.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547524/
![]()
